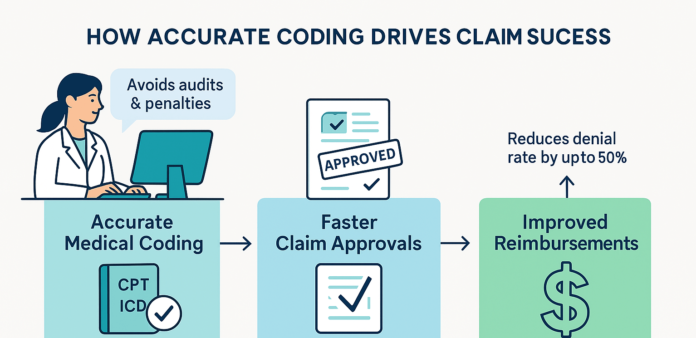
Accurate Coding Strategies to Improve Claim Approvals and Maximize Reimbursements
Medical coding sits at the heart of modern healthcare administration, influencing both patient care quality and the financial stability of medical practices. As providers navigate the complex healthcare landscape, precise and thorough coding becomes a non-negotiable factor that can dramatically increase claim approvals and, by extension, reimbursement rates. Despite its critical importance, many practices still struggle with coding inaccuracies, leading to claim denials, lengthy appeals, and compromised cash flow.
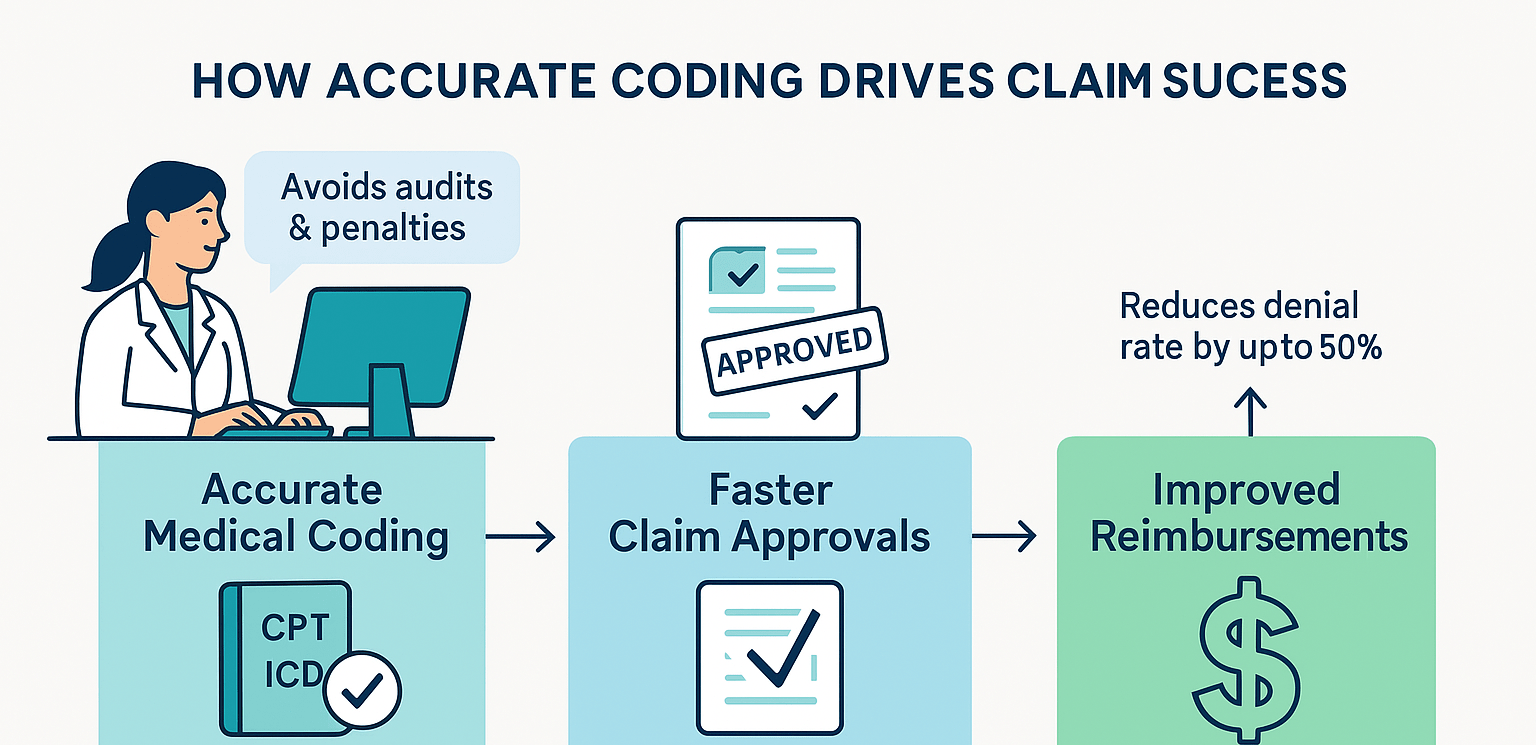
This article delves into how accurate medical coding improves claim approvals, elevates reimbursements, and enhances financial performance. We’ll explore compelling statistics, walk through a brief case study, and provide best practices to elevate your practice’s coding accuracy. Whether you run a small clinic or manage revenue cycle operations for a large hospital system, these insights will help you optimize coding processes and ultimately boost financial health.
1. Why Medical Coding Accuracy Matters
Medical coding is more than just a back-office function; it transforms patient care details into standardized alphanumeric codes used on insurance claims. Precision in coding directly impacts how insurers interpret the services rendered and the legitimacy of reimbursement requests.
-
Claims Approval Rate
Each submitted claim undergoes automated and manual reviews by payers. If coders misrepresent services—intentionally or inadvertently—by using incorrect codes, the claim may be denied. These denials not only delay reimbursements but also consume valuable staff time in correcting and resubmitting claims.
-
Compliance and Audit Risks
Under-coding results in lost revenue, while over-coding or unbundling can lead to audits and penalties. Both government and private insurers continuously monitor patterns that could signal fraudulent or wasteful billing. Accurate coding ensures compliance and guards against costly legal complications.
-
Patient Satisfaction
Accurate coding helps deliver transparent bills. When patients see clear, consistent billing that matches their treatment and insurance coverage, it boosts trust in the provider. Conversely, frequent billing errors damage reputation and patient loyalty.
2. The Direct Financial Impact: Industry Statistics
Numerous studies underscore the enormous financial implications tied to medical coding. Here are some attention-grabbing metrics that put the importance of accurate coding into perspective:
- Denial Rates: According to the American Medical Association (AMA), claims denials can range anywhere from 5% to 15%. A significant portion of these denials stem from coding inaccuracies, including incorrect codes, missing modifiers, or inappropriate bundling.
- Administrative Costs: A study by the Council for Affordable Quality Healthcare (CAQH) estimates that around $31 billion could be saved annually in administrative costs if provider organizations adopt more accurate and standardized processes, including streamlined coding workflows.
- Revenue Loss: Data from the Medical Group Management Association (MGMA) indicates that coding errors can cost a practice 3% to 5% of net revenue—a significant slice for any organization. Correct coding can reclaim these potential losses, channeling them back into direct patient care.
These statistics confirm that the financial stakes are high. A meticulously coded claim can expedite reimbursement and reduce overhead costs. On the other hand, poor coding practices create a ripple effect of rework, higher administrative costs, and cash-flow bottlenecks.
3. How Accurate Medical Coding Raises Claim Approvals
One of the most notable benefits of enhanced coding precision is an immediate uptick in the claim approval rate. Here’s why:
3.1 Consistent Use of Updated Codes and Guidelines
Medical coding is an ever-evolving domain. Each year, CPT (Current Procedural Terminology), ICD-10-CM (International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification), and HCPCS (Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System) codes undergo changes. New codes get introduced, outdated ones retire, and guidelines shift.
Best Practice: Create a coding compliance calendar to stay abreast of annual updates. Regularly attend coding seminars or subscribe to official newsletters from the AMA or AAPC (American Academy of Professional Coders). Ensuring your coding staff is up to date significantly lowers the risk of claims being denied due to outdated or incorrect codes.
3.2 Proper Level-of-Service Coding
Evaluation and Management (E/M) services are a huge component of most claims. Coders must understand guidelines for selecting the correct level of service—particularly with the recent E/M coding changes that emphasize medical decision-making and total time.
Case in Point: If your documentation suggests a moderate level of complexity, but the coder only bills a low-level E/M service, you forfeit potential revenue. Conversely, if you submit a higher-level service than documented, insurers may flag and reject or downcode it, which triggers scrutiny of subsequent claims as well.
3.3 Thorough Documentation to Support Codes
Payers demand solid documentation to justify billed services, especially for high-value procedures or complex treatments. With accurate, detailed documentation in the patient’s chart, coders can confidently select the proper codes.
Best Practice: Establish a documentation-check process. Clinicians and coders should collaborate so the final note in the Electronic Health Record (EHR) contains all pertinent details—medical necessity, start and stop times, relevant diagnoses, and any complexity factors.
4. Real-World Case Study: Improving Denial Rates Through Coding Accuracy
A mid-sized orthopedic practice in the Midwest faced chronic struggles with its denial rate, hovering at around 12%. Dissecting denial analytics revealed that many rejections came from inaccurate coding, especially for complex surgical procedures.
4.1 The Intervention
- Training and Certification: The practice sent three coders for certification in advanced orthopedics coding through the AAPC.
- Collaborative Documentation Review: Coders met weekly with surgeons to address discrepancies between operative notes and billed codes.
- Implementation of Coding Software: They invested in specialized software that auto-suggested appropriate codes based on the physician’s operative notes.
4.2 The Outcome
Within six months:
- The denial rate dropped from 12% to 6%, effectively halving denial-related costs.
- Accounts Receivable (A/R) days improved by 20%, speeding up cash flow.
- The practice’s net revenue saw a 4% increase, purely attributable to more accurate coding.
This case highlights how focusing on one aspect of the revenue cycle—coding—can have a monumental impact on the bottom line.
5. The Ripple Effect on Reimbursements
Accurate coding doesn’t just result in initial approvals; it also propels other revenue cycle metrics. Here’s how:
5.1 Reduced Appeals and Rework
Incorrect coding leads to rework—claims staff must correct mistakes and resubmit. Each denial also extends the payment timeline and inflates administrative overhead. When claims go through the first time without error, you save employee hours, mailing costs, and follow-up calls.
Statistic: Industry estimates suggest that 65% of claim denials are never resubmitted, meaning the healthcare facility forfeits that revenue. Accurate first-pass submissions ensure claims don’t fall through the cracks.
5.2 Optimized Reimbursement Levels
Certain codes provide higher reimbursements when properly documented and justified. For instance, bundling codes incorrectly can reduce the overall claim value. Correct unbundling—only when permissible—unlocks potential revenue for distinct services delivered. Similarly, using complexity-based E/M coding accurately ensures you receive appropriate payment for the care provided.
5.3 Enhanced Payer Relationships
When claims from a specific practice repeatedly arrive with errors, payers may apply additional scrutiny, slowing the claim processing. Conversely, payers appreciate consistency and accuracy, often leading to quicker approvals. Over time, accurate coding fosters an environment of trust, beneficial for both claim approvals and contract negotiations.
6. Common Coding Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Despite best intentions, certain pitfalls frequently arise in medical coding. Recognizing these red flags is the first step toward curbing them.
-
Undercoding to Avoid Scrutiny
Some practices err on the side of caution, choosing lower-level codes instead of accurately representing higher-complexity services. This leads to lost revenue and underestimates the care delivered. Regular internal audits can reveal discrepancies where codes don’t reflect actual services rendered.
-
Overcoding or Unbundling
Overstating services raises red flags among payers. While unbundling is permissible under specific conditions (like distinct procedures for separate anatomical sites), misusing unbundling codes can prompt denials or audits. Coders should thoroughly understand National Correct Coding Initiative (NCCI) edits to avoid these issues.
-
Inconsistent Documentation
If there’s a mismatch between physician notes and the codes billed, payers can reject claims. Maintain consistency by standardizing the documentation process. Encourage providers to detail each service, supporting every code with a clear narrative.
-
Not Staying Current with Guidelines
Each year, code sets evolve. The AMA’s CPT code updates may add or remove codes, while ICD-10-CM frequently includes refinements to diagnosis codes. Missing these changes leads to an avalanche of denials. Regular refresher courses and official coding bulletins are essential for staying updated.
7. Best Practices for High-Precision Coding
To truly harness the benefits of accurate coding, organizations must integrate it into their culture and workflows. Here are some actionable best practices:
7.1 Invest in Ongoing Education
- Certifications: Encourage coders to maintain certifications from reputable bodies like AAPC or AHIMA (American Health Information Management Association).
- Cross-Training: Educate providers on basic coding principles so they understand how their documentation directly affects billing. Regular feedback loops between coders and clinical staff lead to continuous improvement.
7.2 Use Advanced Technology
- EHR Integration: Modern EHRs feature built-in coding engines that suggest potential codes based on encounter details. While these suggestions won’t replace a trained coder, they serve as a strong starting point.
- Coding Analytics: Software with analytics dashboards can pinpoint recurring denial trends, commonly used modifiers, or frequently overlooked code changes. This real-time insight allows you to tackle problems before they escalate.
7.3 Standardize Documentation Processes
Inconsistent documentation spawns confusion and errors. A standardized, codified documentation system helps:
- Create Uniform Templates: Tailor these templates by specialty (e.g., cardiology, orthopedics) to ensure all essential clinical details are captured.
- Adopt Checklists: Encourage clinicians to run through a short checklist each time they complete a patient note, ensuring that no relevant detail is omitted.
7.4 Regular Internal Audits and QA
- Randomized Chart Audits: Each quarter, select a random sample of charts to scrutinize. Compare coded claims to actual clinical documentation. Identify trends or coding errors and fix them promptly.
- Feedback Mechanism: Coders who spot repeated documentation issues can escalate these concerns to team leaders or providers. Timely feedback fosters an atmosphere of continuous quality enhancement.
8. Enhancing the Bottom Line: A Holistic Approach
Accurate coding is only one piece of the larger puzzle of revenue cycle management (RCM). Additional factors like patient registration, insurance eligibility checks, clean claim submissions, and denial management collectively shape your practice’s financial health.
- Eligibility Verification: Ensuring insurance details are correct at the front desk reduces the likelihood of rejections from inactive policies or coverage gaps.
- Prompt Charge Capture: If your billing or coding team doesn’t capture charges quickly, the risk of incomplete documentation or missed codes escalates.
- Efficient Denial Management: Even with high coding accuracy, denials happen. A well-defined workflow for addressing and resubmitting denials maximizes your recovery of legitimate claims.
A cohesive, integrated RCM system ensures accurate coding feeds directly into claim submissions, enabling faster approvals, robust analytics, and lower overhead costs.
9. Sustaining and Growing Your Revenue Gains
Once accurate coding practices are in place and you see improvements in approval rates and revenue, the challenge shifts to maintaining and growing these gains. Healthcare coding evolves continuously, and your strategies must keep pace.
-
Benchmarking
Compare your denial rate, reimbursement per encounter, and coder productivity to industry standards. The MGMA and HFMA (Healthcare Financial Management Association) often release specialty-specific benchmarks. Use these to measure if you’re leading or trailing the industry.
-
Scenario Planning
Healthcare legislation and payer contracts can change quickly. Scenario planning helps you anticipate transitions—like telehealth expansions or new procedure codes—and train your staff ahead of time.
-
Coders as Key Stakeholders
Recognize coders as vital contributors rather than back-office staff. Involve them in strategic discussions about billing, compliance, and service expansions, thereby leveraging their expertise to minimize revenue risks.
10. Conclusion
Accurate medical coding is not a peripheral task—it is a fundamental driver of financial sustainability for healthcare organizations. By blending updated code sets, thorough documentation, and best practices in training and auditing, practices can achieve significant improvements in claim approvals and reimbursement rates. The ripple effect of this accuracy also cultivates stronger relationships with payers, lowers overhead expenses, and enhances patient satisfaction.
Whether you’re a solo practitioner or part of a large, multi-specialty group, the path toward more accurate coding begins with solid education, collaborative communication, and data-driven improvements. As demonstrated by both national statistics and real-world examples, the rewards for getting coding right are clear: greater financial stability, optimized patient care delivery, and a foundation for long-term growth in a fast-evolving healthcare environment.
Accurate coding isn’t just about preventing errors—it’s about unlocking the full potential of your practice’s revenue streams while ensuring the billing process remains compliant, transparent, and patient-centric. By investing in robust coding initiatives today, you set the stage for ongoing financial success and sustained excellence in patient care tomorrow.